With its Q3 GDP growth rate falling to 4.6%, China reduces the 1-year & 5-year LPR by 25 basis points, major sectors continue to grapple; analysts stress on fiscal support.
As the world’s second largest economy experiences slowed growth, China cuts key interest rates on Monday keeping in line with its formerly announced monetary policies.
What’s Changed?
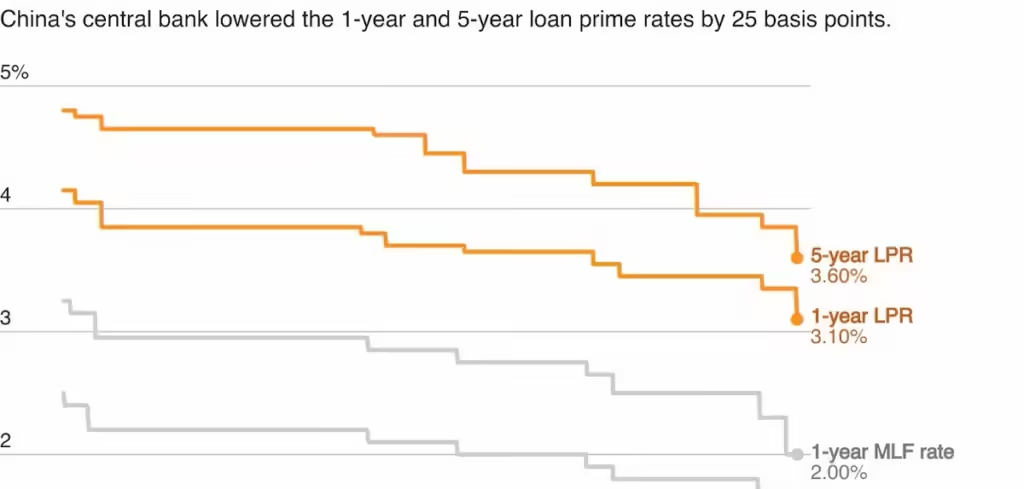
The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) lowered the one-year Loan Prime Rate (LPR) to 3.1% (previously 3.35%), the five-year LPR to 3.6% (from 3.85%). The 1-year LPR acts as a benchmark for corporate loans while the 5-year LPR is essential for mortgage loans. These rates were previously cut by 10 basis points in July, 2024.
As China continues efforts to stimulate the economy, the July rate cuts were followed by a series of interest rate cuts in September. The PBOC slashed the reverse repo rate, also called the seven-day reverse purchase agreements, by 20 basis points, to 1.5%. It had furthermore decreased the Medium-Term Lending Facility (MLF) rate by 30 basis points, to 2.0%.
While the US Fed interest rate cuts by 0.5% motivates the PBOC to ease its monetary policy, further slashes could risk a weaker yuan and reduced lender’s profitability.
As per one of China’s economist at the U.K. research firm Capital Economics, Zichun Huang, “monetary easing policy alone is unlikely to drive a significant turnaround in credit growth.”
Economic Challenges: Declining Loan Activity and Growth
A slowdown in the growth rate has been an obstacle for the Chinese economy. China’s GDP rose by just 4.6% YoY in the third quarter of 2024, which was its lowest growth rate since early 2023. The non-manufacturing sectors have also suffered, with activity falling to its lowest level since December 2022, while manufacturing activity has been declining for five months in a row.
Chinese banks fell short of market forecasts in September, extending 1.59 trillion yuan ($224 billion) in new yuan-denominated loans, according to data issued by the PBOC. This demonstrates the difficulties the financial industry faces in facilitating loan expansion despite declining interest rates.
“A meaningful turnaround in economic growth would require a larger fiscal response,” economist Zichun Huang mentioned on a research note on Monday.
Deflationary pressures necessitate Fiscal stimulus
With its Consumer Price Index (CPI) growth remaining below 1% since March 2023, experts contend that a more robust fiscal response needs to be taken to bring about stabilization in the economy.
According to the central bank of China, a number of fiscal policy changes are in progress to stabilize the economy. A number of support initiatives have been announced by officials in recent weeks, but many specifics are still unknown. China’s top decision-making body, the Politburo of the Communist Party, has committed to “necessary fiscal spending” in order to stabilize the country’s faltering real estate market and meet its growth objective of about 5% by 2024.
Nonetheless, questions remain regarding these measurements’ efficacy. According to recent surveys, including one by Nikkei, analysts predict that China’s GDP would expand by 4.8% in 2024, a minor decrease from earlier projections of 4.9%.
Image Source: Daily Equity – Pan Gongsheng, Governor of the People’s Bank of China, during a rare news conference on Tuesday. Credit- Adek Berry/Agence France-Presse | LSEG Workspace-Reuters 2024





